New Ways Southern Florida Can Tackle Climate Change-related Flooding
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Academic
A group of architecture students at the University of Toronto tapped into their creativity, planning and design skills to reimagine new ways southern Florida can tackle climate change-related flooding, rising water levels and salt water entering canals and corroding existing infrastructure.
Their ideas include plans for communities under threat of flooding to relocate behind a giant arc-like sea wall that could double as a civic monument, a network of complex canals built in public rights-of-way with specialized plants to treat water pollutants in agricultural areas, and a series of fresh water catchment basins in a neighbourhood where salt water is intruding into the groundwater aquifers.
The master's students who are specializing in architecture, landscape architecture and urban design at the John H. Daniels Faculty of Architecture, Landscape, and Design presented nine proposals to a team of local planning and architecture experts and officials from Florida's Broward County.
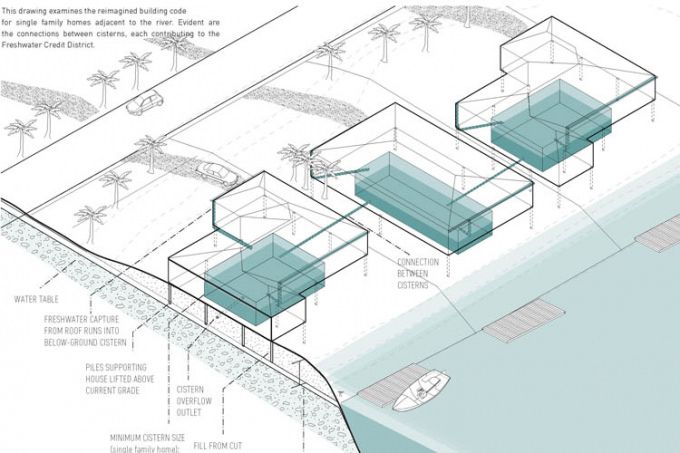
As sea level rises, salt water intrudes into existing aquifers, limiting the fresh water supply in Fort Lauderdale. A student proposal calls for a new network of freshwater cisterns and raising the riverbank with berms to allow residents to keep living at the water’s edge (illustration by Leslie Norris and Natalie Schiabel )
The southeast Florida region, just north of Miami, has been struggling with rising water levels – a recent report showed sea levels rising six times faster than average – as well as an onslaught of hurricanes and ongoing development in flood-prone areas.
“It’s the Trojan Horse,” declared Barbara Blake Boy, executive director of the Broward County Planning Council, about one proposal to convert an existing drainage system into a process by which water can be treated for pollutants using specific plant species that can metabolize toxins from the soil and water runoff.
“This compared to the existing structure is amazing. If I could, I would hire you,” added Maribel Feliciano, assistant director of the county's environmental protection and growth management department.
The Florida county, which abuts the Everglades and includes Fort Lauderdale, has been working with Assistant Professor Fadi Masoud to look at large-scale environmental issues and the role of planning policies and tools in the region.
For the third-year master’s class, Masoud and Assistant Professor Elise Shelley, who has experience studying flooding issues in Louisiana after Hurricane Katrina, asked students to come up with design and zoning solutions for the south Florida county.
The students researched parts of the region, looking at the limitations of the stormwater management system of levees and canals and constraints of the zoning code, as well as the dynamic qualities of the area like rising tides and precipitation.
They chose topics such as affordable housing, beaches, parking lots, mangroves and wetlands. Then, looking at contemporary climate resilience designs, they began thinking of strategies they could propose. Many of the students travelled to the region for a four-day site visit in November where they met with local officials and went on walking tours of various sites they had researched.
“We did a lot of analysis because for us to understand the lifestyle in Florida was a stretch,” said Leslie Norris, who along with Natalie Schiabel proposed a series of freshwater catchment basins in a neighbourhood and called for raising the riverbank with berms to allow residents to keep living at the water’s edge.
“It was really important to understand the challenges they’re facing and constantly facing, and yet aren’t moving out. If we want something to be implemented, it has to be familiar enough that people wouldn’t be afraid of it, that they wouldn’t discredit it from the get-go. So our idea allows people to live at the edge of the river but not be worried about flooding. It allows them to maintain their lifestyle.”
Read full article and see more photos: University of Toronto
Media
Taxonomy
- Integrated Urban Water Management
- Flood Management
- Urban Water
- Water Management
- Urban Water Supply
- Urban Water Infrastructure
- Flood prediction
- Flood Risk Management
- Graphic Design
1 Comment
-
FLOODS CAN BE WARNED
Annually in the world, the number and destructiveness of floods is increasing. The causes of floods are increased precipitation, regulation of releases and destruction of reservoirs, global warming.
No wonder they say that you can not enter into the same river twice. The rivers continuously raise the level of bottom sediments. The movement of water blurs the shore in its endless current, but most of the bottom melts in floods, when water washes into the river everything that lies on the coastal territories - loose soil, sand, clay, various objects and masses of waste of human activity. These accumulations most of all gather below the settlements, forming underwater dams
The outflow of water from the coast occurs, mainly, in such places. They are invisible from the land, but the capacity of rivers decreases within and below towns and cities along the current. Therefore, floods and heavy precipitation are flooding with the destruction of buildings, roads and everything else.
If these submarines are removed, the water outflow from the shores, at least, will move downstream, beyond the boundaries of populated areas.
For this, first of all, it is necessary to measure the depths of the rivers where the waters leave the shores, reveal the dimensions of the rifts and, instead of stacking sandbags and building dams, it is necessary to deepen these sections of the rivers immediately after and during the floods. It is possible to plan in advance the places of floods and to take them away from habitation and constructions. This is possible on the rivers of lowland slopes. On rivers with a large incline floods can be completely excluded.
Existing technologies of dredging are based on excavation, bulldozer cleaning, suction and dredging with expensive serial equipment with pollution of coastal areas and, incredibly, with great financial and material costs. Modern dredgers with a capacity of 100 - 800 kW, as well as their lease are not available to every coastal economy. Giant monsters on the river consume rivers of fuel and pollute the environment, for example: [1]
The great Austrian hydraulic engineer Victor Schauberger once wrote that rivers can self-clean.
Indeed, this is possible if the bottom of the rivers is formed in such a way as to give the flow of water a spiral motion. In fact, the natural movement of water in the river tends precisely to this form of flow - meandering - a gradual and continuous change in the riverbed. In this case, rather large bends of the river are obtained, constantly increasing the total width of the floodplain. The consequence of the expansion are the collapse of the coast, the agricultural areas are being cut, houses and buildings are being destroyed.
Developments have been developed that use the forces of the river to form the river bed and river bed, within specified limits, with specified depths for passing ships, with straightening bends, and controlling water flow. There are possibilities of influencing meandering processes by the simplest means. Manufacture and operation of such facilities are available to small coastal farms that suffer from floods, collapse of shores, shallowing of fairways.
Work to deepen the rolls should be started during and immediately after floods - with strong water movements to prevent floods next year. In the low period, in the summer, the effectiveness of such work is reduced because the water flows in the rivers are decreasing, and some rivers are completely dry.
The proposed method of influencing bottom sediments by the current itself is based on the constraint and control of part of the stream to influence bottom sediments. Devices change and concentrate river flows, without requiring any third-party energy at all. The technological process is carried out by concentrating and directing a part of the stream to pre-selected places of the channel, creating erosion and deposition zones of bottom sediments. Depending on the parameters of the river, the devices are controlled from the shore by cables or supplemented with mobile transport means. Structurally, the devices depend on the thickness of the streams, the width and depth of the river.
New facilities can affect the bottom and coast without using energy sources. Passive devices made of shields, reinforced and controlled by rope block systems or mobile floats, can straighten river beds in pre-designed forms.
There is also a development on this principle more complicated, with the implementation of all known dredging and more - an entirely new technology for underwater works is being created.
A device has been developed that can stand firmly on the bottom and control the flow of water. A device to change the buoyancy and sail, ensure its free movement on the surface of the water. It is possible to supplement it with serial devices for carrying out any known hydraulic engineering works: search and recovery of sunken objects, use of dredges, cutting of surface and underwater tree branches and trunks of trees, washing and lifting of a dewdrop and drowned objects. Management and concentration of flows create absolutely new opportunities not only for the formation of the riverbed. There is a new technology of underwater works, for example, sorting of bottom sediments, with carrying out on the surface of finished fractions, minerals, for example, gold. Flow control almost does not require energy. The recognized patent cleanness of a technical solution, the logical sequence of known essential features of technical solutions that are necessary, and all taken together, are sufficient for the given object to be operational. Tests of individual elements of micromodels of the proposed device on small rivers and trays were conducted, which showed the result. Design work and tests are needed to test and demonstrate the effectiveness of the new method in full-flow river conditions. The first experience on a natural object can start a widespread deepening of the rifts on all rivers where floods occur and warn them in the near flood. The designs of such devices are developed for each type of water body. From shallow rivulets to great rivers, such as the Irtysh, the Urals, the Mississippi and the Amazon. The same problem occurs in the deltas of rivers when they flow into lakes and seas. Gradual sedimentation of the channels and the delta duct lifts their bottom, raising the water level. Shipping dies off, new channels appear, new areas are flooded and swamped, water is spent on impregnating new areas and evaporation. All this ultimately leads to the fact that the lakes dry up, for example, the Aral Sea, on the turn of Balkhash. The proposed devices can save water from spreading and fumes, narrow deltas, restore shipping. To save water for the summer period, it is customary to build reservoirs based on dams and dams. Practice shows that abnormal precipitation leads to the breakthrough of such dams and floods. The reasons leading to this are also the long-term siltation of the reservoir itself by deposits from rivers. Periodically, it is necessary to clean the bowl of the reservoir from sediments. The proposed principle of cleaning the bottom of rivers can be applied here. Strategically building reservoirs, by damaging rivers with dams, is a crime against nature and a high risk of flooding when dams are destroyed. To save the water in a low water, it is enough to dig and deepen the stretches - the existing depths. Deepening of existing reservoirs to the required volumes of accumulation can allow to drain previously flooded areas and eliminate dams - the main sources of man-made disasters. There are several additional additions that create new opportunities, not only in preventing floods, but also in developing new technologies for working under water. Applications: 1. Description of the patent1. Eurasian (21) (13) Patent Office (12) DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION TO THE EURASIAN APPLICATION (43) Application publication date: (51) Int. Cl.KZ2009 / 017 (KZ) 2009.09.07HALIDULLIN OLEG KHANYSHEVICH (KZ) METHOD OF CLEANING AND DEEPENING RUSEL RIV FROM DEPENDENT DEPOSITS EASY FOR IMPLEMENTATION A1 The invention relates to hydraulic engineering and can be used for cleaning river beds and canals from nano-owls. In the method for cleaning and deepening river beds from the bottom sediments by the eroding flow of water, which is created by a mobile water-resistant device with stream-guiding elements, the eroding water flow is created by installing a water-resistant device with stream-guiding elements on the floater mainly at its bottom. This creates a washout zone under the bottom of the floating device. Floating means are moved along the channel at a rate that provides erosion of bottom sediments. Before the cleaning and deepening of the channel, the relief of the bottom sediments is determined. Undiluted part of bottom sediments are destroyed by mechanical action of additional devices placed on the water-resistant device. The water-diffusive device with stream-guiding elements contains longitudinal ribs fixed mainly on the bottom part of the floating means, the jet-guiding elements are made in the form of shields mounted on the end parts of longitudinal ribs with the possibility of adjusting the gap between them. The surface of the ribs, the bottom of the floating device, the surface of the stream-guiding elements form a cavity above the surface of the bottom of the river. Cutters in the form of plowshares are made with the possibility of changing the direction of their edges. Cutters in the form of screws or rotors are equipped with drives. The drives of the augers or rotors are made in the form of blades driven into the rotation by a stream of water. 2. A method for preventing flooding and river water flow control during the period of flooding and the device for its implementation. Patent number RK: 26962 Published: 15.05.2013 Author: Khalidullin Oleg KhanysevichFormula / Abstract The invention relates to hydrotechnical construction and can be used to prevent flooding and management water flow of the river during the period of flooding. The technical result when using the proposed invention is to provide the possibility of erosion of the rifts with the provision of river capacity for the movement of vessels along the paved paths, excluding the formation of floods on the river. The water levels in adjacent reaches are determined with the location of the banks, The flow of water is directed to rolling, and the management of the river's water flows during flooding is provided by laying the fairway by moving to dostesniteliyuyu device along the riverbed along the trajectory of the future fairway. The waterproof device is made in the form of rigidly connected among themselves parallel oriented vertical floating shields, and for the fairway in the device additionally introduced adjustable flexible connections that change the location of the water-resistant device in the longitudinal and pseudo transverse movement of the water flow of the river directions.3. The method of clearing sediments and deepening river beds and the device for its implementation: US Patent No. 87062Author: Kusym Kusyim Duskaev, Vitaly Salnikov, Khalidullin Oleg KhanysevichFormula / Abstract The invention relates to hydraulic engineering and can be used to clean river beds and canal channels. The invention is to develop a method and to create a device using the speed of the river in the most optimal way. The technical result of the proposed method is simplification, and ptimizatsiya one of the existing methods of cleaning river beds and canals, increasing its functionality. Thus, there are opportunities to prevent floods using inexpensive innovative techniques. The Case for Conducting Research and Development Works